Welcome to our informative article on the warning signs of magnesium deficiency. Did you know that more than 50% of the U.S. population is deficient in magnesium? It’s true! Factors such as soil depletion, processed foods, and demineralized water can contribute to this widespread deficiency. Magnesium plays a critical role in muscle and nerve function, energy production, and bone health. Identifying the signs of low magnesium levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Muscle cramps and tension
- PMS symptoms
- Insomnia
- Constipation
- Low mood
These are just a few of the warning signs that could indicate a magnesium deficiency. Keep reading to learn more about the other symptoms and how to address them.
Risk Factors for Magnesium Deficiency
When it comes to magnesium deficiency, there are certain risk factors that can increase your likelihood of experiencing low magnesium levels. Being aware of these risk factors can help you recognize the signs and symptoms of magnesium deficiency and take necessary steps to address it.
Diet low in magnesium-rich foods
Eating a diet that lacks magnesium-rich foods is one of the primary risk factors for magnesium deficiency. Foods such as dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes are rich sources of magnesium. However, processed foods and a diet high in refined sugars and fats often do not provide adequate magnesium intake.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome, can interfere with the absorption of magnesium in the intestines. As a result, individuals with these conditions may be at a higher risk of developing magnesium deficiency.
Excessive alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to magnesium deficiency. Alcohol has diuretic properties, increasing urine production and causing the body to excrete more magnesium. Additionally, alcohol can impair the absorption of magnesium in the intestines, further exacerbating the deficiency.
Certain medications
Some medications can impact magnesium levels in the body. Diuretics, commonly prescribed for conditions such as high blood pressure and heart failure, can increase urinary excretion of magnesium. Other medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics, can also interfere with magnesium absorption.
Aging
As we age, our bodies may become less efficient in absorbing and retaining magnesium. This, combined with potential age-related changes in diet and increased medication use, can contribute to magnesium deficiency.
Pregnancy
Pregnant women have increased magnesium requirements to support fetal development. If maternal magnesium intake is inadequate, the body may draw on its own stores, potentially leading to magnesium deficiency. Pregnancy-related nausea and vomiting can also further deplete magnesium levels.
Chronic stress
Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s magnesium balance. Stress activates the release of stress hormones, which can lead to increased urinary excretion of magnesium. Prolonged stress can also affect dietary habits and make it more challenging to maintain a balanced diet, potentially contributing to magnesium deficiency.
To mitigate the risk of magnesium deficiency, it is essential to prioritize a well-rounded diet that includes magnesium-rich foods and consider supplementation if necessary. Additionally, managing stress levels, reducing alcohol consumption, and discussing medication-related concerns with a healthcare provider can help maintain optimal magnesium levels.
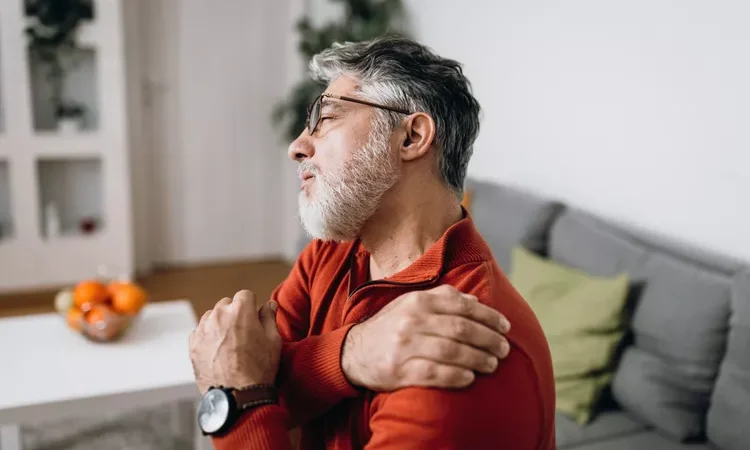
Muscle Cramps and Tension
Muscle cramps and tension can be uncomfortable and disruptive to your daily activities. Did you know that these symptoms could be signs of magnesium deficiency? Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle function, and when levels are low, it can result in muscle cramps and tension.
For men in particular, muscle cramps and tension can be a common indicator of magnesium deficiency. Men may experience these symptoms due to higher muscle mass and increased physical activity, which can lead to a higher demand for magnesium.
So, if you often find yourself struggling with muscle cramps or feeling tense, it may be a sign that your body needs more magnesium. By addressing your magnesium deficiency, you can help alleviate these uncomfortable symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
How Magnesium Helps with Muscle Cramps and Tension
Magnesium plays a significant role in muscle contraction and relaxation. It helps regulate calcium levels, which are essential for muscle function. When there is a magnesium deficiency, calcium can accumulate in muscle cells, leading to prolonged contraction, spasms, and cramps.
By ensuring an adequate intake of magnesium, you can support healthy muscle function and reduce the occurrence of cramps and tension. Magnesium acts as a natural muscle relaxant, helping to calm muscle fibers and prevent the involuntary contractions that cause cramps.
Increasing Your Magnesium Intake
There are various ways to increase your magnesium intake and address magnesium deficiency. Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet is a good starting point. Some excellent food sources of magnesium include:
- Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale
- Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds
- Legumes like chickpeas, lentils, and black beans
- Whole grains, including brown rice and quinoa
- Avocados
However, if your diet alone cannot provide enough magnesium or if you have a severe deficiency, you may consider magnesium supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right dosage and form of magnesium supplement for you.
Remember, addressing magnesium deficiency not only helps alleviate muscle cramps and tension but also supports overall muscle health and function. Taking steps to ensure adequate magnesium intake can contribute to your overall well-being and help you lead an active, pain-free lifestyle.
PMS
Many women experience symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) leading up to their period. While PMS can vary from woman to woman, magnesium deficiency may play a role in exacerbating these symptoms. During the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, magnesium levels tend to be lower, which can contribute to PMS-related discomfort.
Supplementing with magnesium may help alleviate PMS symptoms, providing relief from bloating, cramping, tenderness, and moodiness. Magnesium has a calming effect on the body and can help regulate hormone levels, which can lead to a more comfortable and balanced menstrual cycle.
If you experience severe or persistent PMS symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can provide personalized advice on the appropriate magnesium supplementation dosage and address any underlying issues.
“I used to struggle with intense PMS symptoms every month, but since I started taking magnesium supplements, I’ve noticed a significant reduction in bloating and mood swings. It has really made a difference in my overall well-being.”
Benefits of Magnesium for PMS Relief:
- Reduces bloating and water retention
- Relieves muscle cramps and tension
- Helps stabilize mood swings and irritability
- Supports hormone balance
- Improves sleep quality
Insomnia
If you find yourself tossing and turning at night, struggling to fall asleep, magnesium deficiency could be a contributing factor. Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s sleep-wake cycle, and low levels of this essential mineral can disrupt your natural sleep patterns.
One of the key ways that magnesium influences sleep is through its impact on melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate your sleep and wakefulness. Insufficient magnesium levels can interfere with the production and release of melatonin, making it harder for you to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Fortunately, addressing magnesium deficiency may help improve insomnia symptoms and promote better quality sleep. By increasing your magnesium intake through diet or supplementation, you can work towards rebalancing your body’s sleep mechanisms and restoring a healthy sleep routine.
Ensuring an adequate magnesium level is essential not only for improving sleep but also for overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any major changes to your diet or starting any new supplements. They can help you determine the appropriate dosage and address any underlying issues that may be contributing to your insomnia.
Constipation
Magnesium deficiency can cause constipation due to its ability to relax muscles in the stomach and intestines.
When the body lacks the necessary amount of magnesium, it can lead to difficulty in passing stools and infrequent bowel movements.
Magnesium is often used as a laxative to support regular bowel movements, as it helps to soften the stool and promote healthy digestion.
If you are experiencing constipation and suspect magnesium deficiency as the cause, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Increasing your intake of magnesium-rich foods, such as leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, may also help alleviate constipation symptoms.
Additionally, magnesium supplements are available, but it is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen.

| Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency | Signs of Low Magnesium Levels |
|---|---|
|
|
Low Mood
Magnesium deficiency can have a significant impact on your mood. As a critical regulator of the nervous system, magnesium plays a vital role in maintaining optimal mental health. When levels of magnesium are low, you may experience symptoms of stress and low mood.
Research has linked magnesium deficiency to increased levels of anxiety and depression. This essential mineral is involved in the production and function of neurotransmitters, which are responsible for transmitting signals in the brain. Without adequate magnesium, the neurotransmitter pathways may be disrupted, leading to imbalances that contribute to feelings of sadness and irritability.
In addition, magnesium plays a pivotal role in supporting sleep quality. Insomnia and poor sleep can significantly impact your mood, leaving you feeling more vulnerable to stress and negative emotions. Low levels of magnesium have been associated with sleep disturbances, such as difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep.
To address low mood and support your mental well-being, it’s crucial to ensure you’re getting enough magnesium. If you’re experiencing symptoms of stress, anxiety, or depression, consider incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet or exploring magnesium supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Magnesium Deficiency Warning Signs: Low Mood
- Feelings of stress and anxiety
- Depression or persistent sadness
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Impaired sleep quality
- Irritability or mood swings
As magnesium deficiency affects the nervous system, it’s important to address any warning signs promptly. By ensuring adequate magnesium intake, you can help support your mood, reduce stress levels, and promote overall mental well-being.
Decreased Bone Density
Ensuring healthy bones and teeth is vital for overall well-being, and magnesium plays a crucial role in achieving this. It is involved in the absorption and metabolism of calcium, a key mineral for bone health. Unfortunately, deficiency in magnesium can lead to decreased bone density, making your bones more susceptible to fractures.
Signs you need more magnesium:
- Brittle bones
- Frequent fractures
- Poor teeth health
Signs of low magnesium levels:
- Weakness in bones
- Inability to maintain bone density
- Elevated risk of osteoporosis
To support your bone health and prevent complications, it’s essential to ensure an adequate intake of magnesium. Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on supplementation and incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet.
Proper magnesium levels are not only essential for bone health but also play a significant role in overall bodily functions. In the next section, we will explore how magnesium deficiency can contribute to headaches and migraines.
Headaches and Migraines
If you frequently experience headaches or migraines, it might be a sign of low magnesium levels. Magnesium plays a crucial role in blood vessel function and neurotransmitter release in the brain, which are both important factors in managing headaches and migraines.
When magnesium levels are insufficient, it can lead to blood vessel constriction and increased release of certain neurotransmitters that contribute to pain sensation. This can result in recurring headaches or migraines that may range from moderate to severe in intensity.
To alleviate these symptoms, it’s essential to address magnesium deficiency. You can increase your magnesium intake through dietary sources such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Additionally, magnesium supplements are available and can be beneficial for individuals with low magnesium levels.
Experiencing frequent headaches or migraines can significantly impact your quality of life. If you suspect magnesium deficiency as a contributing factor, consult with a healthcare professional to evaluate your magnesium levels and discuss appropriate treatment options. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods and supplements can help support optimal brain function and reduce the frequency and severity of headaches and migraines.
Blood Pressure Imbalance
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is crucial for overall cardiovascular well-being. Magnesium, an essential mineral, plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure. When your body lacks sufficient magnesium, it can contribute to blood pressure imbalances, including high blood pressure or hypertension.
High blood pressure, if left uncontrolled, can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of low magnesium levels, as they may indicate a magnesium deficiency that could potentially impact blood pressure regulation.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Magnesium Levels
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Weakness and fatigue
- Irritability and mood changes
- Irregular heartbeat
In men, magnesium deficiency can exhibit additional signs such as low testosterone levels, decreased libido, and reduced muscle strength.
Proactively addressing magnesium deficiency can help support healthy blood pressure levels. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is wise to consult a healthcare provider who can evaluate your magnesium levels and provide appropriate guidance.
Implementing dietary changes that include magnesium-rich foods, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, can support healthy magnesium levels. If necessary, your healthcare provider may recommend magnesium supplements to help restore and maintain optimal levels in your body.
“Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is essential for the prevention and management of hypertension. It is important to recognize and address magnesium deficiency to support cardiovascular health.”
By addressing magnesium deficiency and prioritizing blood pressure management, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Conclusion
Magnesium deficiency can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. Recognizing the symptoms of magnesium deficiency is crucial in addressing the issue promptly. Common signs to look out for include muscle cramps, low mood, fatigue, and irregular bowel movements. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if magnesium deficiency is a contributing factor.
Fortunately, addressing magnesium deficiency is relatively simple. Increasing your magnesium intake through a combination of diet and supplementation can help replenish your body’s magnesium levels and promote better health and wellness. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Additionally, consider incorporating a magnesium supplement into your daily routine to ensure adequate intake.
Remember, maintaining optimal magnesium levels is essential for proper muscle function, bone health, and overall well-being. By being aware of the symptoms of magnesium deficiency and taking proactive steps to address it, you can improve your quality of life and support your body’s vital functions.