Magnesium deficiency is a common health problem, affecting millions of Americans. Low magnesium levels can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. It’s important to recognize the warning signs and take steps to address this deficiency. In this article, we will explore the various symptoms of magnesium deficiency and how it can affect your body.
Magnesium plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including muscle function, energy production, and bone health. It is involved in hundreds of reactions throughout the body, making it an essential mineral for overall health. When you are deficient in magnesium, it can lead to various symptoms and health issues.
Here are 11 warning signs of magnesium deficiency:
Difficulty Getting Through Workouts
If you find yourself struggling to complete workouts that you used to do with ease, it could be a sign of magnesium deficiency. Low magnesium levels can affect muscle function and energy production, making it more challenging to stay active and reach your fitness goals.
Muscle Weakness
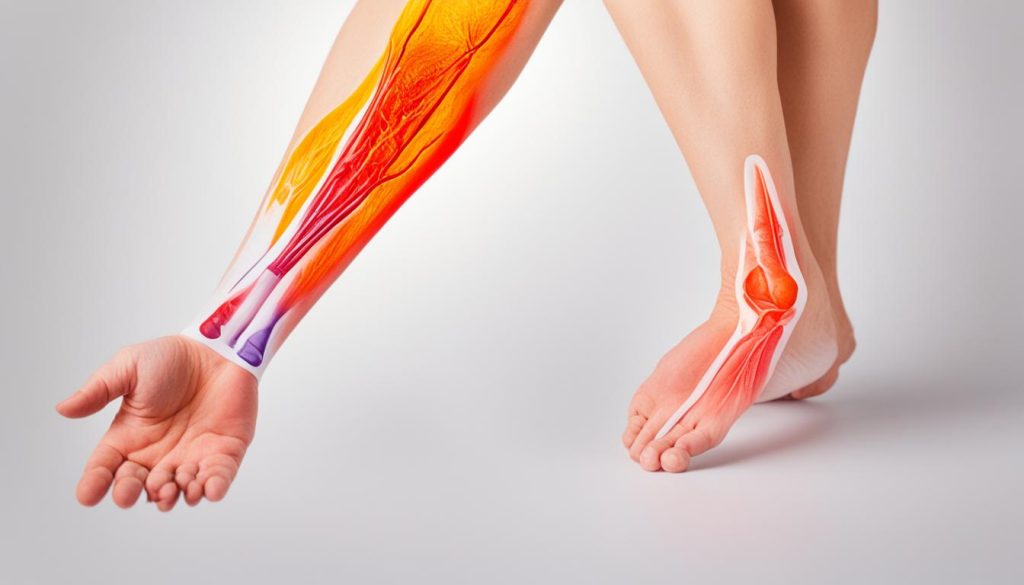
Magnesium is crucial for proper muscle function, and when there is a deficiency, it can lead to muscle weakness. If you experience unusually weak or tired muscles, it may be a sign that your magnesium levels are low.
Muscle Cramps
Frequent muscle cramps can be an indication of magnesium deficiency. Low levels of magnesium can disrupt the balance of calcium and potassium in muscle cells, leading to cramping and twitching. If you experience frequent muscle cramps, consider getting your magnesium levels checked.
Bone Density Loss or Osteoporosis
Magnesium deficiency is a risk factor for bone density loss and osteoporosis. Since a significant portion of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones, low levels of magnesium can contribute to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Maintaining adequate magnesium levels is essential for optimal bone health.
High Blood Pressure
Elevated blood pressure can be influenced by magnesium deficiency. Research suggests that low magnesium levels may contribute to increased blood pressure, which can raise the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. Monitoring your blood pressure and ensuring sufficient magnesium intake is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Inflammatory Issues
Magnesium deficiency has been associated with increased levels of inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can contribute to various health conditions, including asthma and autoimmune disorders. Increasing your magnesium levels may help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Trouble Sleeping
Struggling with sleep disturbances can be a sign of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium plays a role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythm and promoting relaxation. If you have trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or experience restless sleep, it may indicate a need for additional magnesium.
Feeling Depressed
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of depression and mood disorders. Adequate magnesium levels are vital for neurotransmitter function and stress response, making it crucial for mental well-being. If you experience persistent feelings of sadness or mood changes, consider checking your magnesium levels.
Feeling Anxious
Anxiety disorders can be influenced by low magnesium levels. While more research is needed to understand the exact relationship between magnesium and anxiety, many individuals report feeling calmer and more relaxed after supplementing with magnesium. If you frequently experience anxiety or have been diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, ensuring sufficient magnesium intake may be beneficial.
Increased Migraines
Magnesium deficiency has been associated with increased migraine frequency. If you suffer from migraines, it may be worth considering your magnesium levels. Some individuals find relief by incorporating magnesium supplements into their treatment plan.
Recognizing the warning signs of magnesium deficiency is the first step towards maintaining optimal health. If you suspect that you may have low magnesium levels, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss possible supplementation or dietary changes.
Key Takeaways:
- Magnesium deficiency can significantly impact your overall health and well-being.
- Warning signs of magnesium deficiency include difficulty with workouts, muscle weakness, muscle cramps, bone density loss or osteoporosis, high blood pressure, inflammatory issues, trouble sleeping, feeling depressed or anxious, increased migraines, and loss of appetite.
- Incorporating magnesium-rich foods and considering supplementation may help address magnesium deficiency.
- Consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended to determine the appropriate dosage and form of magnesium supplementation for your individual needs.
- Regularly monitoring your magnesium levels and maintaining a balanced diet can help prevent magnesium deficiency.
Difficulty Getting Through Workouts
Are you struggling to make it through your workouts? It could be a sign of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium is a vital nutrient for muscle function and energy production, playing a crucial role in your exercise performance. When you have low levels of magnesium, it can lead to decreased potassium levels in your muscle cells, resulting in muscle weakness and fatigue.
If you find yourself suddenly exhausted during workouts that you used to breeze through, it’s worth considering whether low magnesium levels may be a contributing factor. Magnesium deficiency can make it difficult for your muscles to perform optimally, hindering your overall exercise performance and leaving you feeling fatigued.
To ensure you’re getting enough magnesium to support your workouts, consider incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet or discussing magnesium supplementation with your healthcare provider. By addressing potential magnesium deficiency, you may find yourself with the energy and stamina to power through your workouts and achieve your fitness goals.
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness can be a symptom of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle function, and low levels of magnesium can lead to decreased potassium levels in muscle cells, causing muscle weakness and fatigue. If your muscles feel unusually weak or tired, it may be a sign of magnesium deficiency.
“When there is a deficiency of magnesium in the body, muscle weakness can occur. This is because magnesium is required for proper muscle contraction and relaxation. Without sufficient magnesium, the muscle cells may not function optimally, leading to weakness and fatigue.”
It’s important to address magnesium deficiency to support muscle health and overall well-being. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet, such as spinach, almonds, and avocados, can help ensure an adequate intake. Additionally, magnesium supplements may be recommended by a healthcare professional to correct deficiency.
Magnesium-Rich Foods
| Foods | Magnesium Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Spinach | 79mg |
| Almonds | 270mg |
| Avocado | 29mg |
Adding these magnesium-rich foods to your diet can help support muscle function and prevent muscle weakness. However, if you suspect magnesium deficiency, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps are a common symptom of magnesium deficiency. When your magnesium levels are low, it can disrupt the balance of calcium in your nerve cells, causing muscle cramps and twitching. These cramps can range from mild calf cramps during walking to severe muscle spasms or even seizures.
If you frequently experience muscle cramps, it may be a sign of magnesium deficiency. Increasing your magnesium intake through diet or supplementation can help alleviate muscle cramps and restore proper muscle function.
| Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency | Effects on Muscle Cramps |
|---|---|
| Muscle weakness and fatigue | Magnesium deficiency can lead to decreased potassium levels in muscle cells, resulting in muscle weakness and increased susceptibility to cramps. |
| Electrolyte imbalance | Low magnesium levels can disrupt the balance of calcium and potassium in muscle cells, making them more prone to cramping. |
| Nerve signal disruption | Magnesium is necessary for proper nerve function. A deficiency can affect the transmission of nerve signals to the muscles, leading to cramps and twitches. |
If you’re suffering from muscle cramps due to magnesium deficiency, consider incorporating magnesium-rich foods such as spinach, almonds, and bananas into your diet. Additionally, you may want to consult with a healthcare professional about the possibility of magnesium supplementation to address your deficiency and alleviate muscle cramps.
Bone Density Loss or Osteoporosis
Magnesium deficiency is a risk factor for bone density loss and osteoporosis. Approximately 60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones, where it helps maintain bone health. Low magnesium levels can lead to hypocalcemia, a condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood, and increase the risk of osteoporosis. If you have magnesium deficiency, you may be at higher risk for bone density loss and related conditions.
| Condition | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Low magnesium levels | Fragile, brittle bones | Calcium and magnesium supplements, weight-bearing exercise, hormone therapy |
| Bone Density Loss | Magnesium deficiency | Weakening of bones | Dietary changes, magnesium supplementation, exercise |
H3: Key Takeaways
- Magnesium deficiency increases the risk of bone density loss and osteoporosis.
- About 60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones.
- Low magnesium levels can cause hypocalcemia, leading to weakened bones.
- Treatment options for bone density loss and osteoporosis include calcium and magnesium supplements, weight-bearing exercise, and hormone therapy.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects many individuals. Did you know that magnesium deficiency may contribute to the development of high blood pressure?
Magnesium plays a vital role in our bodies, including regulating blood pressure levels. Low magnesium levels have been found to raise blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health issues.
Regularly monitoring your blood pressure is crucial in maintaining good cardiovascular health. If you have been diagnosed with hypertension, or if you are concerned about your blood pressure levels, magnesium supplements may be beneficial in lowering your blood pressure.
Research has shown that magnesium supplementation can help reduce blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. Magnesium helps relax and dilate blood vessels, promoting better blood flow and reducing the strain on the heart.
It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or making changes to your treatment plan. They can provide you with personalized guidance and ensure that magnesium supplementation is suitable for your specific situation.
| Benefits of Magnesium for High Blood Pressure | How to Obtain Magnesium |
|---|---|
| 1. Helps relax blood vessels | 1. Eat magnesium-rich foods such as leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. |
| 2. Promotes better blood flow | 2. Consider magnesium supplements under the supervision of a healthcare professional. |
| 3. Reduces strain on the heart | 3. Ensure a balanced diet with adequate magnesium intake. |
By incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet and considering magnesium supplementation, you may be able to support healthy blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with hypertension.
Key Takeaways:
- Magnesium deficiency may contribute to high blood pressure.
- Low magnesium levels have been found to raise blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health issues.
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure is important, and magnesium supplements may help lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is also essential in managing blood pressure levels. Stay proactive about your cardiovascular health and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Inflammatory Issues
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to increased levels of inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is a complex process that plays a role in various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Studies have shown that individuals with chronic inflammation may experience a reduction in inflammation when taking magnesium supplements.
Research has indicated that magnesium has anti-inflammatory properties, helping to regulate the body’s inflammatory response. Magnesium plays a vital role in immune function and the production of anti-inflammatory molecules. By addressing magnesium deficiency, individuals may be able to mitigate the impact of inflammatory issues on their overall health and well-being.
In addition to chronic inflammation, magnesium deficiency may also be associated with specific inflammatory conditions such as asthma. Researchers have found that individuals with asthma often have lower magnesium levels, and severe asthma cases may be related to magnesium deficiency.
It is important to note that magnesium alone may not be the sole solution for managing inflammatory issues. However, ensuring adequate magnesium levels through diet and supplementation may complement other preventive measures and lifestyle interventions to promote overall health and reduce the risk of inflammatory diseases.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
| Food | Magnesium Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Spinach | 157 |
| Chard | 154 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 123 |
| Almonds | 75 |
| Black beans | 60 |
| Avocado | 58 |
| Yogurt | 49 |
| Banana | 32 |
 Note: The magnesium content mentioned above is approximate and may vary depending on factors such as growing conditions and preparation methods.
Note: The magnesium content mentioned above is approximate and may vary depending on factors such as growing conditions and preparation methods.
Trouble Sleeping
Magnesium deficiency can contribute to trouble sleeping. Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythm, muscle relaxation, and sleep neurotransmitters such as GABA.
When you have low magnesium levels, it can lead to difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep. Insomnia, characterized by trouble sleeping, is a common symptom of magnesium deficiency.
To promote better sleep quality, it is beneficial to supplement with magnesium. By elevating your magnesium levels, you can help regulate your body’s sleep-wake cycle, relax your muscles, and support the production of sleep-inducing neurotransmitters.
Feeling Depressed
Feeling depressed? Your mood may be influenced by magnesium deficiency. Research suggests that low magnesium levels can increase the risk of depression and mood disorders. Magnesium plays a vital role in improving your response to stress and alleviating symptoms of depression, particularly in women going through menopause.
If you are experiencing unexplained mood changes or find yourself feeling down, it’s worth considering if magnesium deficiency could be a contributing factor.
To give you a visual representation of the relationship between magnesium deficiency and depression, here’s a table showcasing key findings:
| Research Study | Key Finding |
|---|---|
| Study 1 | Magnesium supplementation resulted in a significant reduction in depressive symptoms in participants with low magnesium levels. |
| Study 2 | Individuals with low magnesium levels had a higher prevalence of depression compared to those with normal magnesium levels. |
| Study 3 | Higher magnesium intake was associated with a lower risk of depressive symptoms in women in a large-scale population study. |
As you can see, there is a clear link between magnesium deficiency and depression. Taking steps to ensure adequate magnesium levels in your diet or discussing supplementation with a healthcare provider may help improve your mood and overall well-being.
In addition to the table, here’s an image related to the topic:
Feeling Anxious
Low magnesium levels have been associated with an increased risk of anxiety disorders. While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between magnesium deficiency and anxiety, many individuals take magnesium to promote a sense of calmness and relaxation. If you experience frequent anxiety or have been diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, magnesium levels may be worth considering.
Magnesium plays a crucial role in the body, including the regulation of neurotransmitters and hormones that can influence mood. Research has shown that magnesium deficiency may contribute to feelings of nervousness and restlessness, common symptoms of anxiety. By maintaining adequate magnesium levels, you may potentially alleviate some of these symptoms.
While it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, magnesium supplementation or dietary changes may be beneficial for managing anxiety symptoms. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can also help support optimal magnesium levels.
Benefits of Magnesium for Anxiety:
- Promotes relaxation and calmness
- Supports proper neurotransmitter function
- Regulates stress response
- Assists in maintaining balanced hormones
“Magnesium is like the Swiss Army knife of minerals when it comes to anxiety.” – Dr. Carolyn Dean, MD, ND
While magnesium can be beneficial for managing anxiety, it’s essential to explore holistic approaches and seek professional guidance for a comprehensive treatment plan. Magnesium supplementation should be used as a complementary strategy in conjunction with other evidence-based therapies.
Increased Migraines
If you experience frequent migraines, magnesium deficiency may be a contributing factor. Studies have shown that individuals with migraines are often more likely to have low magnesium levels. Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating blood vessel function and neurotransmitter release, both of which can impact the frequency and intensity of migraines.
Research has suggested that magnesium supplementation can help decrease the frequency and severity of migraines in some individuals. By addressing magnesium deficiency, it is possible to find relief and improve your quality of life.
| Migraine Symptom | Possible Link to Magnesium Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Frequent headaches | Low magnesium levels may increase the likelihood of experiencing migraines. |
| Intense pain | Magnesium deficiency can contribute to the severity of migraines. |
| Light and sound sensitivity | Low magnesium levels may amplify sensitivity to external stimuli during migraines. |
| Nausea and vomiting | Magnesium deficiency may exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms associated with migraines. |
If you suspect that magnesium deficiency may be contributing to your migraines, consult with your healthcare provider. They can help you determine if magnesium supplementation or dietary changes may be beneficial for managing your migraines.
Conclusion
In summary, magnesium deficiency is a common health issue that can have a significant impact on overall well-being. From difficulty with workouts to muscle weakness, cramps, and even bone density loss or osteoporosis, the symptoms of magnesium deficiency can be wide-ranging. Additionally, high blood pressure, inflammatory issues, trouble sleeping, feelings of depression or anxiety, increased migraines, and loss of appetite can all be related to inadequate magnesium levels.
Adequate magnesium intake is crucial for maintaining optimal health. This essential mineral plays a vital role in hundreds of bodily processes and reactions. To address magnesium deficiency, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can help determine the best approach for supplementation or dietary changes. By ensuring you have sufficient magnesium, you can support your overall health and well-being.
If you suspect you may be experiencing magnesium deficiency, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized recommendations and help you address any potential deficiencies. Remember, maintaining a balanced diet and incorporating magnesium-rich foods can also contribute to your overall magnesium intake.