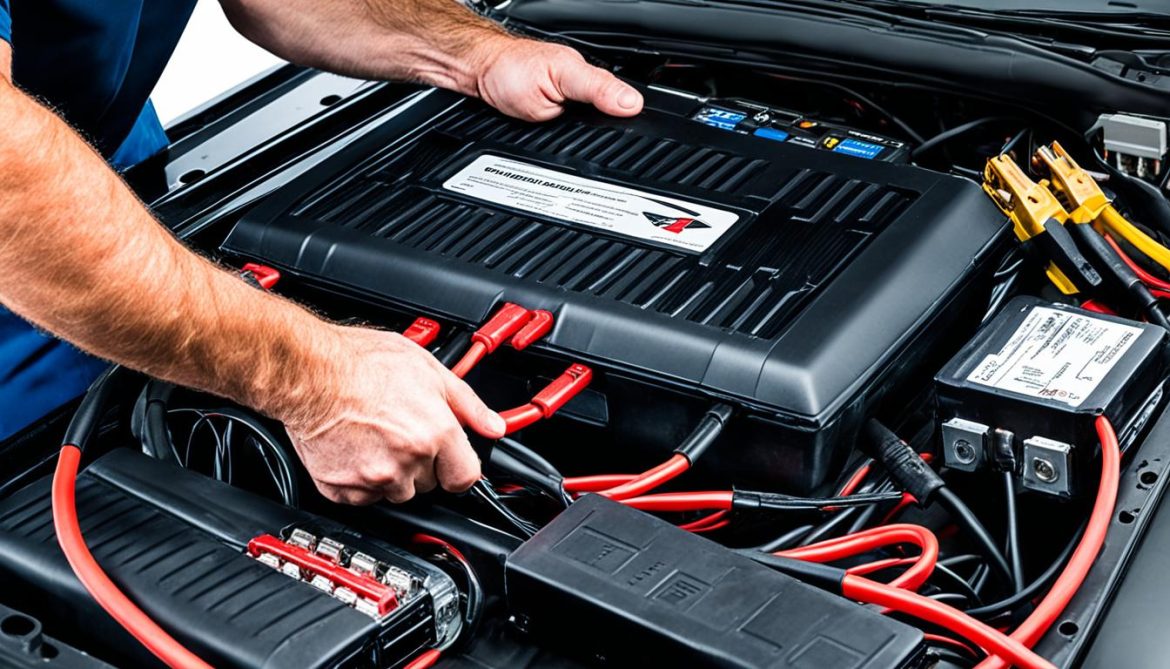
If you own a semi-truck, you may encounter battery issues or breakdowns that require a jump start. Knowing how to jump start a 24 volt system is essential to get your truck back on the road quickly and safely. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process, ensuring a successful boost for your semi-truck.
Key Takeaways:
- Jump starting a 24 volt system requires the right tools and equipment.
- Choose heavy-duty jumper cables designed for large vehicles like semi-trucks.
- Properly position the vehicles and connect the jumper cables to the correct terminals.
- Start the assisting vehicle’s engine and let it run to charge the dead battery.
- Disconnect the jumper cables in the correct order to ensure safety.
Understanding the Right Tools and Equipment
To successfully jump-start a 24 volt system, it is essential to have the right tools and equipment on hand. Using improper tools may lead to ineffective jump-start attempts or even cause damage to the vehicles involved. Here are the essential tools and equipment you’ll need:
1. Heavy-Duty Jumper Cables
Jumper cables are the lifeline for jump-starting any vehicle, and when it comes to 24 volt systems like those found in semi-trucks, heavy-duty jumper cables are a must. These cables are specifically designed to handle the high amperage required to kick-start larger engines. They feature thicker cables and robust clamps to ensure a solid connection between the donor and recipient vehicles. Investing in heavy-duty jumper cables guarantees a successful jump start without the risk of damage.
2. Safety Glasses
Safety should always be a top priority when working with any automotive electrical system. Wearing safety glasses not only protects your eyes from potential sparks or debris but also ensures a clear line of sight throughout the jump-start process. Safety glasses act as a necessary barrier between your eyes and any potential hazards, allowing you to focus on the task at hand.
3. Battery Charger or Booster
In some cases, using a battery charger or booster can be an effective alternative to jump-starting a 24 volt system. These devices provide a controlled charge to the dead battery, gradually replenishing its power. A battery charger or booster is especially useful if the semi-truck’s battery is severely drained or damaged. It allows for a safe and efficient recharge without the need for another vehicle.
It’s also a good idea to have additional safety equipment readily available, such as a flashlight and gloves. These items will ensure better visibility and protect your hands from potential electrical shocks or battery acid. Remember, taking the necessary precautions and using the right tools will make the jump-starting process smoother and safer.
| Essential Tools for Jump Starting a 24 Volt System |
|---|
| Heavy-Duty Jumper Cables |
| Safety Glasses |
| Battery Charger or Booster |
Don’t forget to keep these essential tools in your vehicle at all times, as you never know when you might need to jump-start a 24 volt system. Being prepared ensures that you can handle any unexpected situations with confidence and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Jumper Cables
When jump-starting a 24 volt system, selecting the right jumper cables is crucial. The quality and suitability of the cables can greatly impact the success of the jump start. Consider the following factors to ensure that you choose the appropriate heavy-duty jumper cables for your semi-truck:
- Gauge: The gauge of the cables determines their thickness and ability to carry electric current. For a 24 volt system, it is recommended to use jumper cables with a larger gauge, such as 2 gauge or 1/0 gauge, which provide better conductivity and can handle the higher power demand.
- Length: The length of the cables is also important. Opt for cables that are long enough to reach between the two vehicles comfortably. Longer cables allow for better maneuverability and prevent unnecessary strain on the cables.
- Clamps: The clamps on the jumper cables should be sturdy and able to securely attach to the battery terminals. Look for clamps with strong springs and teeth that provide a solid grip. Ensure that the clamps have appropriate openings to fit over the battery terminals of a 24 volt system.
- Cable Insulation: Insulation plays a vital role in protecting the cables from damage and ensuring safety during the jump start process. Opt for jumper cables with thick and durable insulation that can withstand the rigors of heavy-duty use.
By considering these factors, you can select heavy-duty jumper cables that will provide optimal performance and a secure connection for jump-starting your 24 volt system. Remember, investing in quality jumper cables will not only make the jump-start process more efficient but also contribute to the longevity of your cables.
Positioning the Trucks and Connecting the Cables
Properly positioning the trucks and connecting the cables is crucial for a successful jump start. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure an effective and safe process.
Positioning the Trucks
When positioning the vehicles for jump starting, it’s important to ensure that their batteries are in close proximity. Park the assisting vehicle with a functioning battery alongside the semi-truck, making sure they are facing each other and the front ends are as close as possible.
This will allow the jumper cables to reach both vehicles’ batteries without tension or strain. Keep in mind that for safety reasons, both vehicles should be in park with their engines turned off and the parking brake engaged.
Connecting the Jumper Cables
Once the trucks are properly positioned, it’s time to connect the jumper cables. Follow these steps:
- Identify the positive and negative terminals on both batteries. The positive terminal is usually marked with a (+) sign, while the negative terminal is marked with a (-) sign.
- Attach one end of the positive or red cable to the positive terminal of the assisting vehicle’s battery.
- Connect the other end of the positive cable to the positive terminal of the semi-truck’s dead battery.
- Next, connect one end of the negative or black cable to the negative terminal of the assisting vehicle’s battery.
- Finally, connect the other end of the negative cable to a grounded metal surface on the semi-truck’s engine block or chassis. This will help to minimize the risk of sparks near the battery.
Ensure that all connections are secure and snug. Do not let the jumper cables come into contact with any moving parts in the engine compartment.
Refer to the illustration below for a visual representation of the connected jumper cables.
| Assisting Vehicle | + |  |
– | Semi-Truck |
|---|
Remember, proper positioning of the vehicles and correct connection of the jumper cables are crucial steps for a successful jump start. Taking the time to ensure a secure and efficient connection will greatly increase the chances of a smooth and safe jump-start process.
Starting the Trucks and Removing the Cables
Now that the jumper cables are properly connected, it’s time to start the trucks and remove the cables. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth transition:
- Start the Assisting Vehicle: Turn on the engine of the assisting vehicle, which has the fully charged battery. Let it run for a few minutes to allow the battery to transfer power to the semi-truck’s dead battery.
- Monitor Battery Status: Keep an eye on the battery status of both vehicles. You should see an improvement in the charging level of the semi-truck’s battery as it receives power from the assisting vehicle.
- Switch Off Assisting Vehicle: After several minutes, turn off the engine of the assisting vehicle. This will prevent any electrical surges or mishaps during the cable removal process.
- Removing the Jumper Cables: To remove the jumper cables safely, follow these steps:
| Jumper Cable Color | Connection Order |
|---|---|
| Black/Negative Cable (-) | 1. Disconnect the black/negative cable from the assisting vehicle’s negative battery terminal. |
| Black/Negative Cable (-) | 2. Disconnect the black/negative cable from the semi-truck’s negative battery terminal. |
| Red/Positive Cable (+) | 3. Disconnect the red/positive cable from the assisting vehicle’s positive battery terminal. |
| Red/Positive Cable (+) | 4. Disconnect the red/positive cable from the semi-truck’s positive battery terminal. |
By following these steps, you can safely start the trucks and remove the jumper cables without any issues. Remember to always prioritize safety and handle the cables with care to avoid any electrical shocks.
Troubleshooting and When to Call a Professional
If your semi-truck fails to start even after several attempts, it’s possible that there may be underlying issues with the electrical system. In such cases, it’s important to troubleshoot the problem and determine whether it requires professional assistance. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you diagnose and address potential issues:
1. Check for Damage or Corrosion on the Cables
Inspect the jumper cables for any visible damage or corrosion. Damaged cables can result in a weak or incomplete connection, preventing the battery from receiving sufficient charge. If you notice any frayed wires or rusted clamps, it’s advisable to replace the cables before attempting another jump start.
2. Ensure a Solid Ground Connection
A solid ground connection is essential for a successful jump start. Make sure the clamp of the negative cable is securely attached to an unpainted metal surface on the semi-truck’s engine block or chassis. This ensures proper grounding and allows for the smooth transfer of power between the vehicles.
3. Recognize the Signs of a More Serious Issue
- If the semi-truck’s engine cranks but fails to start, it could indicate a fuel delivery or ignition system problem.
- If you hear clicking noises and the engine does not turn over, it may be a sign of a faulty starter motor.
- Dim lights, weak electrical systems, or a battery that continually drains even after jump-starting can indicate a more serious issue with the 24 volt system.
It’s important to recognize these signs as they may require the expertise of a professional mechanic or electrician to resolve the problem effectively.
4. When to Call a Professional
While jump-starting a 24 volt system can often resolve battery-related issues, there are situations where professional assistance is necessary. It is recommended to call a professional if:
- The semi-truck’s battery shows signs of physical damage or leakage.
- You are unable to determine the cause of the electrical problem or troubleshoot the system effectively.
- Repeated jump-start attempts fail to start the vehicle.
Calling a professional ensures that the issue is properly diagnosed and addressed, minimizing the risk of further damage to the electrical system.
Remember, troubleshooting a 24 volt jump start requires patience and caution. Always prioritize your safety and seek professional help when needed. Now let’s move on to the final section to wrap up our comprehensive guide on jump-starting a 24 volt system.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now learned expert advice on how to safely jump start a 24 volt system. By following the step-by-step guide and taking necessary precautions, you can resolve battery issues efficiently. Remember, your safety is paramount, so always prioritize it throughout the process.
When it comes to jump-starting a 24 volt system, it is essential to have the right tools and equipment, such as heavy-duty jumper cables, safety glasses, and a battery charger or booster. Properly positioning the vehicles and connecting the cables correctly is crucial for a successful jump start. Once the cables are connected, starting the trucks and removing the cables in the correct order is equally important.
If you encounter any issues during the process, don’t hesitate to troubleshoot. Check for any damage or corrosion on the cables and ensure a solid ground connection. In case you face continuous difficulties or suspect a more serious problem with your 24 volt system, it is advisable to seek professional help.
Now that you are equipped with the knowledge and precautions for jump-starting a 24 volt system, you can confidently address battery issues in a safe and efficient manner. Remember to always prioritize your safety and seek professional assistance when needed. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a seamless jump-starting experience for your semi-truck.
FAQ
What tools and equipment do I need to jump start a 24 volt system?
You will need heavy-duty jumper cables, safety glasses, a flashlight, and a battery charger or booster.
What factors should I consider when choosing jumper cables for a 24 volt system?
Factors to consider include gauge, length, clamps, and cable insulation to ensure optimal performance and a proper connection.
How do I properly position the trucks and connect the cables for a jump start?
Ensure the vehicles are close to each other and connect the jumper cables to the positive and negative terminals of the batteries, grounding them to the semi-truck’s engine block or chassis.
What is the process of starting the trucks and removing the cables?
Start the assisting vehicle’s engine and let it run for a few minutes to charge the semi-truck’s dead battery. Then remove the jumper cables in the correct order to ensure a safe disconnect.
What should I do if the semi-truck doesn’t start after multiple attempts?
Check for damage or corrosion on the cables and ensure a solid ground connection. If the issue persists, it may be necessary to seek professional help.
Are there any important precautions to take when jump starting a 24 volt system?
Yes, prioritize your safety at all times, and if you are unsure or uncomfortable with the process, seek professional assistance.