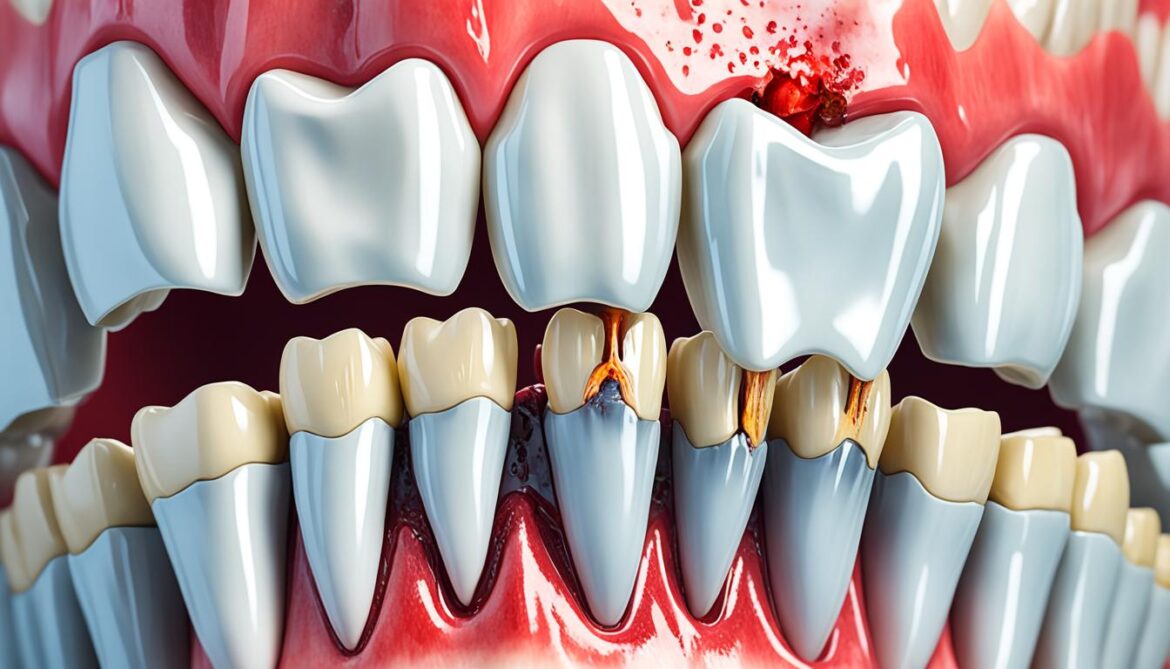
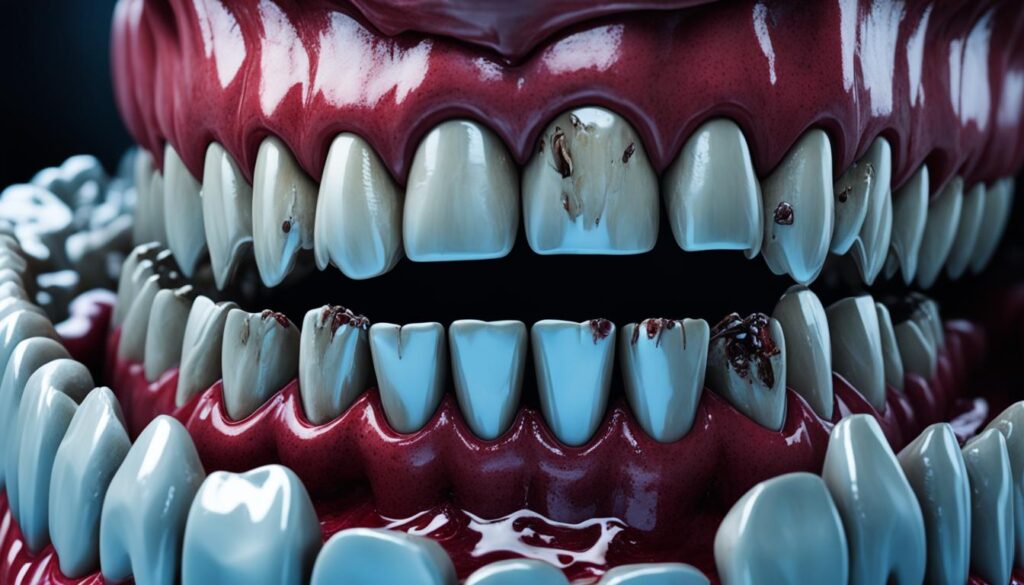
A tooth infection can have severe complications if left untreated, ranging from spreading to other parts of the body to life-threatening conditions like sepsis. Understanding the risks and recognizing the signs of a tooth infection is crucial for prompt dental care and preventing serious consequences. In this article, we will explore the timeline and risks associated with tooth infections, as well as the importance of seeking immediate medical attention for dental emergencies.
Key Takeaways:
- Untreated tooth infections can lead to severe complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
- Knowing the signs and symptoms of a tooth infection can help you identify when to seek immediate dental care.
- Prompt treatment of tooth infections is crucial in preventing life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
- Good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and reducing sugary food intake can help prevent tooth infections.
- Antibiotics may be used as part of the treatment for tooth infections, but they are not typically a definitive solution on their own.
Understanding Tooth Infections
Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses, are pockets of pus that form in different parts of the tooth or surrounding gum, bone, or soft tissues due to bacterial infection. They typically occur due to severe tooth decay, injury, or gum disease.
Symptoms of a tooth infection include:
- Persistent toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Sensitivity to pressure while biting or chewing
- Swelling in the face or cheek
- A pus pocket or bump on the gums
- Tender and swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Bad breath or foul taste in the mouth
These infections can start as localized discomfort but can quickly progress and spread to the root of the tooth, leading to a painful dental abscess. If left untreated, the infection can extend beyond the mouth, impacting the neck, jaw, or other parts of the body such as the heart or brain.
Signs and Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
A dental abscess, also known as a tooth infection, can cause a range of signs and symptoms that should not be ignored. Recognizing the early warning signs is essential to seek immediate medical attention and prevent the infection from progressing further.
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Throbbing toothache: A persistent and intense toothache that may radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear.
- Tooth sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
- Pressure sensitivity: Discomfort or pain when biting or chewing.
- Facial swelling: Swelling in the face or cheek near the affected tooth.
- Pus pocket on the gums: A visible bump or pocket of pus near the tooth.
- Tender and swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature often accompanied by other symptoms.
- Bad breath or foul taste in the mouth: Unpleasant breath odor or taste due to the infection.
It is important to note that these symptoms may vary in severity and can be indicative of other dental conditions. However, the presence of multiple symptoms, especially if accompanied by fever or severe swelling that extends beyond the mouth, should be considered a dental emergency.
Given the potential risks associated with untreated tooth infections, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any combination of these symptoms. Early intervention can help prevent the infection from spreading and minimize the risk of severe complications.
| Signs and Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Throbbing toothache | A persistent and intense toothache that may radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear. |
| Tooth sensitivity | Increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. |
| Pressure sensitivity | Discomfort or pain when biting or chewing. |
| Facial swelling | Swelling in the face or cheek near the affected tooth. |
| Pus pocket on the gums | A visible bump or pocket of pus near the tooth. |
| Tender and swollen lymph nodes | Enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck. |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature often accompanied by other symptoms. |
| Bad breath or foul taste in the mouth | Unpleasant breath odor or taste due to the infection. |
When Does a Tooth Infection Become Life-Threatening?
A tooth infection can become life-threatening when it spreads beyond the tooth and reaches critical areas of the body. The infection can spread through different pathways, such as the bloodstream, leading to a serious condition known as sepsis. Sepsis is a medical emergency that can cause organ failure and be fatal if not treated promptly.
Another potential complication of a tooth infection is the spread of the infection to the brain. Although less common, this can occur when the infection travels through the blood vessels or sinus. Infections that reach the brain can result in severe consequences and may require immediate medical attention.
One particularly dangerous complication to be aware of is Ludwig’s Angina. This condition arises from a tooth or dental infection and progresses rapidly, often blocking the airways and causing breathing difficulties. Ludwig’s Angina is a life-threatening situation that should be treated as an emergency, requiring immediate medical intervention.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a tooth infection, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention if you notice any of the following:
- Fever
- Severe swelling in the face or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing
- Intense pain
Recognizing the signs of a potentially life-threatening tooth infection and seeking prompt medical attention is essential for preventing severe complications and protecting your overall health.
| Life-Threatening Complications of Tooth Infections | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Sepsis | Fever, rapid heartbeat, confusion, shortness of breath, organ failure |
| Infection Spreading to the Brain | Headache, neck stiffness, fever, neurological symptoms |
| Ludwig’s Angina | Swelling in the neck, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, fever |
| Organ Failure | Varies depending on the affected organ |
Treatment for Tooth Infections
Treatment for tooth infections is crucial to eliminate the infection, save the affected tooth if possible, and prevent complications from arising. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the infection and the condition of the affected tooth.
If detected early, antibiotics may be prescribed to help eliminate the bacterial infection. Antibiotics work by killing the bacteria responsible for the infection. However, it’s important to note that antibiotics alone are not typically considered a definitive treatment for dental abscesses. They should be used in conjunction with other dental procedures to address the root cause of the infection.
One common procedure for treating tooth infections is draining the abscess. This involves removing the infected pus through a small incision in the affected area. By draining the abscess, the source of the infection is eliminated, providing relief and preventing further spread.
In cases where the infection has spread to the inside of the tooth, root canal treatment may be recommended. This procedure involves cleaning the interior of the tooth and removing any infected tissues. By removing the infected pulp and sealing the tooth, the infection can be effectively eliminated.
However, if the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, tooth extraction may be necessary. Tooth extraction involves removing the infected tooth to prevent the spread of infection and eliminate the source of the problem.
Prompt treatment is crucial in preventing the spread of infection and the development of serious complications. It is important to seek professional dental care if you suspect a tooth infection to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent further health issues.
By seeking timely treatment for tooth infections, you can eliminate the infection, potentially save the affected tooth, and prevent the development of complications. Remember to follow the advice and guidance of your dental professional to ensure optimal oral health.
Prevention of Tooth Infections
To prevent tooth infections and their potential complications, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential. By following these simple practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing a tooth infection:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to thoroughly clean all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Pay attention to your gum line as well.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria from between your teeth and along the gum line. This helps prevent the formation of dental abscesses and other oral health issues.
- Reduce the consumption of sugary foods and drinks, as they provide a breeding ground for bacteria that can lead to tooth decay and infections. Opt for healthier alternatives and practice moderation.
- Stick to a well-balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. A nutritious diet helps maintain strong teeth and gums, reducing the risk of infection.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Dental professionals can identify early signs of infection or other dental problems, allowing for timely intervention.
By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can prevent tooth infections and promote optimal oral health. Remember, prevention is always better than treatment.
Can Antibiotics Cure a Tooth Infection?
Antibiotics play a crucial role in the treatment of dental infections, but it is important to understand their limitations and consider their role as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
When it comes to a tooth infection, antibiotics are primarily used to control the spread of an existing infection and provide support to the body’s natural defenses in eliminating the bacteria. However, antibiotics alone are not typically a definitive treatment for dental abscesses.
To effectively address a tooth infection, other dental procedures are usually required to eliminate the underlying cause of the infection. These include:
- Root canal treatment: This procedure involves cleaning the inside of the tooth, removing infected tissues, and sealing the tooth to prevent further infection.
- Periodontal treatment: For infections that have spread to the gum tissues, periodontal treatment may be necessary to remove bacteria and infected tissues.
- Tooth extraction: In some cases, if the tooth is severely infected and cannot be saved, extraction may be the best course of action to eliminate the infection.
Over-reliance on antibiotics can contribute to the problem of antibiotic resistance, where bacteria become less responsive to treatment. It is important to use antibiotics judiciously and in conjunction with the necessary dental procedures to ensure effective elimination of the infection and prevent potential complications.
| Pros of Antibiotic Use in Dental Infections | Cons of Over-Reliance on Antibiotics |
|---|---|
|
|
While antibiotics are an important tool in the treatment of dental infections, they should be used in conjunction with other dental procedures to effectively eliminate the cause of the infection. The appropriate course of treatment will depend on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the overall oral health of the individual.
Conclusion
Tooth infections pose serious risks to both oral and overall health. Prompt treatment and proper dental care are crucial in preventing severe complications and the spread of infection to other parts of the body. While rare, death from a tooth infection can be prevented with timely intervention and appropriate dental treatment.
If you suspect a tooth infection or any dental problem, it is essential to consult a dental professional. Delaying treatment for an intense or worsening tooth infection can result in escalated issues. Seeking help from a dentist can ensure the health of your oral and overall well-being.
Remember that dental issues can progress quickly. Timely detection, intervention, and appropriate care are key to effectively managing tooth infections and minimizing their potential complications. Taking care of your dental health through regular check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and reducing sugary food intake can also help prevent tooth infections.
FAQ
How long does it take for a tooth infection to become life-threatening?
The exact timeline for a tooth infection to become life-threatening is difficult to determine as it depends on factors such as the individual’s immune response and the severity of the infection. An infection that enters the bloodstream can become serious within a few days.
What are the signs of sepsis from a tooth infection?
Symptoms of sepsis from a tooth infection include fever, severe swelling, shortness of breath, and difficulty swallowing. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
What are the risks of untreated tooth infection?
Untreated tooth infections can lead to severe complications such as sepsis, the infection spreading to other parts of the body, and even organ failure. It is important to seek dental care to prevent these risks.
What are the symptoms of a dental emergency?
Symptoms of a dental emergency include fever, severe swelling, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, intense pain, and pus pockets on the gums. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
How high are the mortality rates for tooth infections?
While tooth infections can be serious, death from an infection is rare. With timely intervention and proper dental care, tooth infections can usually be effectively managed.
What are the complications of an untreated dental abscess?
Untreated dental abscesses can lead to the spread of infection to other parts of the body, potentially causing sepsis, brain infection, or Ludwig’s Angina, a serious condition that can block the airways.
When should I seek treatment for a tooth infection?
It is important to seek immediate dental care if you have a tooth infection accompanied by fever, severe swelling, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, or intense pain.
What are the consequences of ignoring a toothache?
Ignoring a toothache can lead to the progression of a tooth infection, which can result in severe pain, complications, and even life-threatening conditions. It is crucial to address toothaches promptly.