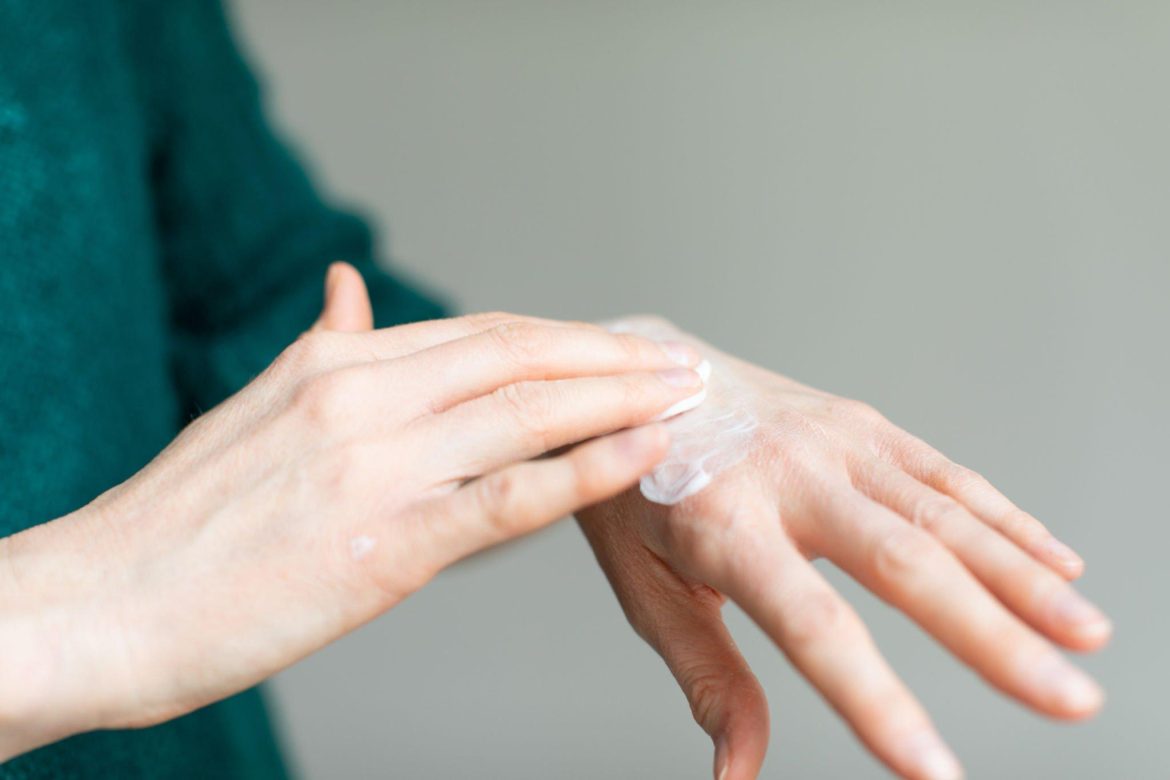
The skin barrier serves as a shield against free radicals and is often compromised by harsh external conditions. Ensure its health with the use of oils, ceramides, and additional products.
Both high-end beauty stores and local drugstores offer a plethora of products designed to preserve and revitalize your skin. These can range from exfoliants and plumpers to moisturizers.
What unites these diverse products is their focus on the skin barrier, the outermost layer of your skin.
So, what is the skin barrier, what role does it play, and what can weaken it?
This piece aims to clarify these questions and discuss measures you can implement to maintain and recover this crucial protective layer.
Defining the Skin Barrier and Its Function
The skin is a complex organ with multiple layers that have distinct roles in defending your body.
The external layer, known as the stratum corneum, resembles a brick wall. It consists of durable skin cells, or corneocytes, held together by lipids acting as mortar. This constitutes your skin barrier.
Within these skin cells, you’ll find components like keratin and natural moisturizers, while the lipid layer houses:
- cholesterol
- fatty acids
- ceramides
This incredibly thin “brick wall” is vital for your survival. It guards against environmental toxins and pathogens that could otherwise penetrate your skin and have detrimental effects.
Moreover, without this skin barrier, your body’s water content would evaporate, resulting in severe dehydration.
Maintaining a healthy skin barrier is critical for optimal bodily function.
Factors That Can Impair the Skin Barrier
Your skin is under constant assault from various external and internal factors that can affect its health, such as:
- extreme humidity or aridity
- allergens, irritants, and pollution
- excessive sun exposure
- strong soaps and detergents
- harsh chemicals
- over-exfoliation or over-cleansing
- steroid medications
- emotional stress
- hereditary susceptibility to skin issues like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Importance of Acid Mantle
Your skin barrier has a slightly acidic pH, which serves as a protective buffer against harmful microorganisms. This acidic environment is essential for many biological interactions that facilitate healing, especially around wounds.
In some health conditions, like diabetes or incontinence, your skin’s pH may change, weakening this protective layer. For such cases, experts advise more acidic skincare products.
Signs of a Compromised Skin Barrier
If your skin barrier is dysfunctional, you may experience:
- dry, flaky skin
- itchiness
- uneven or discolored patches
- acne
- inflamed or sensitive areas
- bacterial, viral, or fungal skin infections
Ways to Maintain and Restore Your Skin Barrier
Considering the importance of your skin barrier and its acidic environment, here are five strategies to keep them both in top condition:
- Streamline Your Skincare Routine If your skincare regimen includes a multitude of products, you might unintentionally be harming your skin barrier. Consult with a dermatologist about essential and effective products.
- Monitor pH Levels A healthy skin pH is around 4.7. Opt for cleansing products that have a pH between 4.0 and 5.0 to maintain this balance.
- Use Plant Oils Certain plant oils can help both restore and hydrate your skin barrier. These oils also offer antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant benefits.
- Opt for Ceramide-Infused Formulas Ceramides are crucial lipids that ensure proper functioning of your skin barrier. Products containing ceramides may improve symptoms like dryness, itchiness, and scaling.
- Utilize Moisturizers with Hyaluronic Acid, Petrolatum, or Glycerin Occlusive moisturizers help prevent water loss and improve barrier function. Humectants like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, honey, and urea can also aid in retaining moisture.