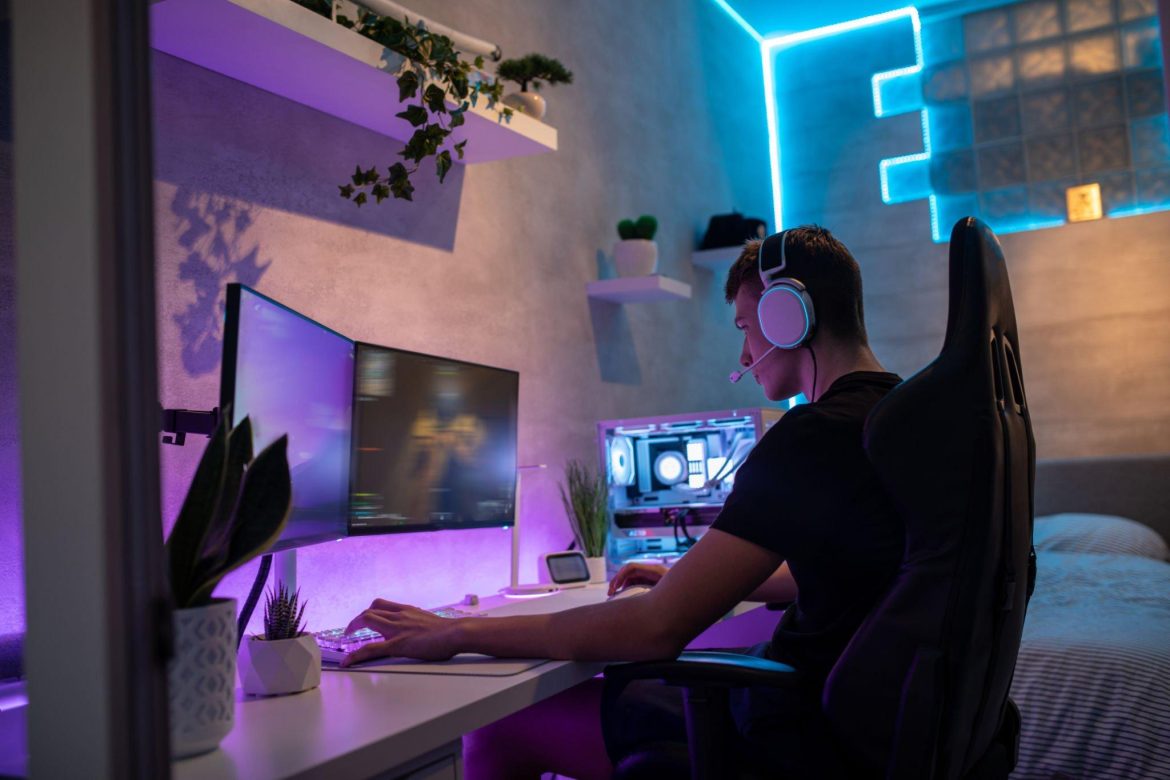
Teens and young adults are immensely attracted to video games, immersing themselves in various virtual environments ranging from mythical realms in “World of Warcraft” to the competitive arenas of “Fortnite” and the creative spaces of “Animal Crossing.” A significant study highlighted that 85% of middle and high school students engaged in video gaming activities in the past year.
Video Gaming: A Cultural Phenomenon with Potential Downsides
While video games offer an avenue for creativity, fantasy exploration, and online interaction with peers, their omnipresence in modern culture might not be entirely advantageous. An alarming 86% of parents believe their children dedicate excessive time to gaming. This raises concerns about potential impacts on the youth’s sleep, social interactions, and mood. The big question arises: How does this widespread gaming culture affect mental health?
Mental Health and Video Games: A Complex Interaction
Video games, like any other form of entertainment, can influence mental health. Numerous factors contribute to gaming’s impact, including the individual’s social life, mental health status, the type of games played, and the duration of gaming sessions. Understanding the multifaceted effects of video gaming, both negative and positive, is crucial.
Negative Mental Health Impacts of Video Gaming
1. Aggression and Violent Games
The violent content in many popular video games might escalate aggression in players. Research presents mixed views, but some studies indicate a link between violent gaming and aggressive behavior, though external factors also contribute significantly.
2. Disruption of Sleep Patterns
Excessive and late-night gaming sessions can severely disrupt sleep quality, which is vital for mental well-being. Such disturbances may exacerbate existing mental health issues.
3. Escapism: A Double-Edged Sword
While video games offer a reprieve from daily stress, overindulgence may lead to unhealthy escapism. This could result in avoidance of real-life challenges and an overreliance on gaming.
4. Gaming and Depression
Excessive gaming, particularly in isolation, is associated with depression. Prolonged gaming sessions and neglect of real-life connections can lead to isolation, a known depression risk factor. Moreover, a link between violent games and depression symptoms has been observed in some studies.
5. Gaming and Social Anxiety
A complex relationship exists between excessive gaming and social anxiety. Gaming may both attract and exacerbate social anxiety, with excessive gamers potentially experiencing increased difficulties in real-life social interactions.
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) and Its Implications
Understanding Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD)
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is often equated with “video game addiction.” It’s a behavioral addiction where gaming interferes significantly with an individual’s daily life. IGD is diagnosed when gaming becomes problematic, affecting the person’s overall functioning.
Symptoms of Internet Gaming Disorder
Some key symptoms of IGD include:
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Feelings of irritability, anxiety, or sadness when not gaming.
- Escapism Through Gaming: Consistently using video games as a means of escape.
- Deception about Gaming Time: Lying to family and friends regarding the amount of time spent on gaming.
- Gaming Over Other Activities: Prioritizing gaming over relationships and other important activities.
- Increased Gaming Time for Pleasure: Needing more gaming time to achieve the same level of satisfaction.
- Negative Impact on Performance: Poor performance at school or work due to excessive gaming.
- Neglect of Personal Hygiene: Reduced attention to personal grooming and hygiene.
- Gaming as Emotional Relief: Using gaming as a means to cope with negative emotions like hopelessness or guilt.
- Difficulty Reducing Game Time: Challenges in cutting down or quitting gaming despite recognizing its negative impact.
Diagnosis of IGD requires the presence of multiple symptoms for over a year. Professional mental health treatment is advised for individuals showing signs of IGD.
IGD and Neurodivergence
Neurodivergent individuals, due to their heightened sensory processing, intense focus on specific interests, and preference for structured routines, may find video games particularly appealing. Studies indicate a potential link between neurodivergence, such as autism spectrum disorders and ADHD, and an increased risk of IGD. However, it’s important to note that not all neurodivergent individuals are prone to problematic gaming, just as some neurotypical individuals may engage in unhealthy gaming habits.
Positive Effects of Video Games on Mental Health
1. Cognitive Enhancements
Video games can enhance problem-solving skills and creativity. Many games require players to think critically, strategize, and solve complex problems, thus potentially boosting cognitive abilities and creativity.
2. Social Connections
Contrary to the belief that gaming is isolating, many modern video games promote social interaction. They offer a platform for players to connect with friends and meet new people, potentially reducing loneliness. Face-to-face social interactions outside gaming, however, remain important.
3. Relief from Stress and Anxiety
For the Gen Z population, grappling with high rates of anxiety, video games can serve as a stress-relief tool. Various types of games, particularly “cozy games,” are found to help alleviate anxiety by providing a distraction and a sense of calm.
4. Combatting Depression
Video gaming can also positively affect individuals dealing with depression. It can act as a mood booster and provide a sense of joy or pleasure, which might be lacking in their lives. The social aspect of multiplayer online games can also help alleviate feelings of isolation associated with depression.