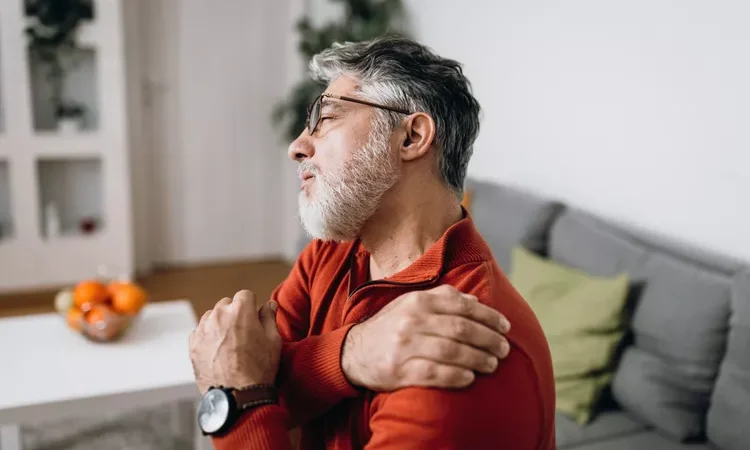
Psoriasis is more than a skin issue; it’s a long-lasting disease that affects your immune system. It changes physical health and life quality. It makes skin cells grow too fast. This leads to psoriasis symptoms showing as scaly, rough patches. These patches can be mild or severe and appear in different places. Learning about these symptoms helps form a good psoriasis management plan. Although we don’t know exactly what causes it, we believe it’s a mix of genes and environment. Knowing possible triggers and using the right care methods can help control it. This lets people with psoriasis keep their skin healthier and manage their condition better.
Key Takeaways
- Psoriasis is an immune-mediated condition that speeds up the lifecycle of skin cells.
- The appearance of psoriasis symptoms can differ significantly among individuals.
- Familial patterns suggest genetics play a role in psoriasis causes.
- Identifying unique triggers is crucial for effective psoriasis management.
- Personalized care routines can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for those with psoriasis.
- Consultation with healthcare providers is key to diagnosing and treating psoriasis effectively.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition. It requires an in-depth understanding to care for properly. It affects many people across the globe. It’s a chronic issue that needs a smart treatment plan.
Defining Psoriasis as a Skin Condition
Understanding psoriasis is key to managing it. It speeds up skin cell turnover, causing quick buildup. This leads to scales, itchy patches, and discomfort, affecting one’s life.
Understanding the Role of the Immune System
Psoriasis involves an overactive immune system. This increases skin cell growth, causing visible issues. Addressing immune misfires is crucial in treatment, helping to ease symptoms and prevent more issues.
Psoriasis: Not a Contagious Disease
Many think psoriasis can spread from person to person, but this is false. It’s important to know this and show kindness to those dealing with it. Despite its looks, it needs understanding and proper care, not fear.
| Skin Cell Growth in Psoriasis | Normal Skin Cell Growth |
|---|---|
| Expedited 3-4 day cycle | Standard 28-30 day cycle |
| Plaque formation and scaling | Even, unnoticeable shedding |
| Itching, burning, and stinging sensations | No discomfort or visible symptoms |
| Potential for psoriatic arthritis and other comorbidities | Few associated secondary conditions |
The Different Types and Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis varies greatly in complexity and type. It’s vital for people to know the psoriasis symptoms to seek psoriasis skin care and psoriasis remedies effectively. Knowing common symptoms helps identify psoriasis. Understanding specific types allows for better treatment plans. We’ll look into general psoriasis symptoms and then detail common forms.
Common Symptoms Across Psoriasis Types
Psoriasis varies, but some symptoms are common. These include red and inflamed skin patches with silver-white scales. People might feel soreness or have dry skin that bleeds. Itching and burning are also frequent, making daily psoriasis skin care challenging. Psoriasis affects emotional health, so treatments must care for both mind and body.
Symptom Variations in Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type. On lighter skin, plaques are pink or red with silvery scales. On darker skin, they’re dark brown and less scaly, causing discoloration. Itching and pain drive people to seek psoriasis remedies. Without treatment, skin may crack and bleed, highlighting the condition’s severity.
Pustular, Guttate, Inverse, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Other psoriasis types have unique symptoms. Pustular psoriasis features white pustules on red skin, often on hands and feet. Guttate psoriasis shows up as salmon-pink dots, usually after certain infections. Inverse psoriasis affects skin folds, creating smooth, red patches prone to irritation. Erythrodermic psoriasis is rare but severe, causing widespread redness and scaling. It’s life-threatening, underlining the urgent need for treatment and effective psoriasis skin care.
Recognizing Psoriasis Causes
Exploring psoriasis causes shows us a mix of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. A faulty immune system causes inflammation and fast skin growth. This results in the distinctive skin plaques. Genetics plays a role, making some people more likely to get psoriasis. But things like skin injuries, stress, and infections can also trigger it.
Lifestyle choices strongly influence psoriasis. What we eat and our habits, like the psoriasis diet, matter a lot. Both alcohol and smoking can make psoriasis worse. So, making better choices can help manage the condition.
Dealing with psoriasis means looking at the big picture. It takes psoriasis medication, diet changes, and new habits. Each person needs a plan that suits their unique challenges and triggers.
| Trigger Factor | Impact on Psoriasis | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Foundational risk factor for psoriasis | Monitor family history; early detection and management |
| Immune System Dysfunction | Direct cause of inflammation and cell turnover | Immunomodulatory medications and therapies |
| Skin Injury or Stress | Can precipitate psoriasis outbreak | Stress management; careful skin care |
| Infection | May trigger immune-mediated skin response | Prompt treatment of infections; vaccination where possible |
| Alcohol and Smoking | Associated with increased risk and severity | Lifestyle modification; cessation programs |
| Diet and Nutrition | Certain foods may worsen inflammation | Personalized psoriasis diet aimed at reducing inflammation |
Managing psoriasis is teamwork between the patient and doctors. It focuses on knowing personal triggers and taking steps to prevent flares. This helps lessen psoriasis’s effects on life.
How Psoriasis Diagnosis is Performed
Identifying psoriasis involves careful steps. Doctors use different methods to make sure they diagnose it correctly. Knowing if someone has psoriasis helps doctors decide on the best way to manage it. They start by closely looking at the symptoms and skin.
The Physical Exam for Psoriasis
A detailed skin exam is what dermatologists or healthcare providers will do. They search for signs like thick, red skin patches with silvery scales. These signs mostly show up on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. If there’s a family history of psoriasis, a diagnosis is more likely.
This exam confirms psoriasis and checks how much skin is affected. Understanding the skin’s condition is key for managing psoriasis well.
Additional Laboratory Tests and Biopsies
Sometimes, the skin exam alone isn’t enough. Then, doctors may run blood tests. These tests help rule out other conditions that look like psoriasis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. A biopsy might be needed too.
In a biopsy, a tiny piece of skin is examined under a microscope. This step is important if the patient’s symptoms are unusual or if there’s no family history of psoriasis. Getting the diagnosis right is crucial. It ensures that the patient receives the best care to improve their life quality.
Understanding the Genetics of Psoriasis
Exploring psoriasis genetics shows how complex it is. Many people carry genes that make psoriasis more likely. Yet, only some will show symptoms. This situation leads us to wonder what sets off psoriasis in these cases. It shows that many genetic factors play a role.
Researchers have found many genes linked to psoriasis. So far, they’ve identified over 80 mutations related to it. This discovery shows psoriasis has a complex genetic basis. Here, we see how genetics and external elements work together. They trigger the inflammation typical of psoriasis.
Learning about these genetic links is crucial. It helps in creating better psoriasis medication. Knowing about genetic factors can lead to personalized treatment. Such treatments could better match a person’s genetic makeup. This could help control symptoms better and possibly prevent psoriasis in those at risk.
Today’s treatments help, but they’re not perfect for everyone. That’s why finding specific treatments is so important. By focusing on the precise genetic issues in psoriasis, new treatments could be developed. These treatments would aim to be more effective and have fewer side effects.
Advances in genetics promise to improve how we treat psoriasis. As we learn more, we expect better treatments to emerge. This knowledge could greatly change how we help those with psoriasis.
Identifying Triggers and Managing Outbreaks
Living with psoriasis means learning what causes your flare-ups. These psoriasis triggers can vary for everyone. They may include environmental factors or lifestyle choices. For example, cold weather might worsen your symptoms. Minor skin injuries, like cuts or bug bites, can also lead to an outbreak. Stress is another big factor that can make psoriasis hard to manage.
To take care of psoriasis, you need to avoid triggers and use effective psoriasis remedies. A good care routine combines steps to prevent flare-ups and ways to treat symptoms when they happen.
- Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress and prevent flare-ups.
- Regular Skin Care: Moisturizing helps stop your skin from getting dry and irritated.
- Mindful Medication: Know which medications might cause an outbreak. Talk about alternatives with your doctor.
- Weather Wisdom: Dress right for the weather. Use humidifiers to keep indoor air moist.
Knowing your personal triggers is key to psoriasis care. Keep a diary of your outbreaks. Note your daily activities and the weather. This can help you see patterns and manage your psoriasis better.
“To manage psoriasis well, adapt to your unique needs. Understand your triggers and embrace self-care.”
In the end, while there’s no cure for psoriasis yet, knowing your triggers and following a care plan can help. This way, you can handle your psoriasis better and live a happier life.
Examining Psoriasis and Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices deeply affect psoriasis. They determine its severity and progress. Being mindful about diet and skincare is essential for managing this condition effectively. Health-focused changes can greatly assist those living with psoriasis.
The Impact of Alcohol and Smoking
Alcohol and smoking worsen psoriasis and make treatments less effective. Reducing alcohol and stopping smoking can improve skin health for people with psoriasis.
Dietary Considerations in Psoriasis Management
Choosing a diet filled with anti-inflammatory foods helps control psoriasis. Such a diet supports medical treatments and eases flare-ups. Focusing on healthy eating is crucial for better skin health and for reducing discomfort from psoriasis.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Psoriasis | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol Consumption | Potential trigger for flare-ups; may decrease treatment efficacy. | Limiting or eliminating alcohol to mitigate negative effects on skin and treatment outcomes. |
| Smoking | Increases risk and severity, particularly pustular psoriasis on hands and feet. | Quitting smoking to reduce risk and improve health. |
| Nutrition | Certain foods may trigger inflammation and worsen symptoms. | Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet to support skin health and reduce symptoms. |
Managing psoriasis is more than just skin treatments. It’s about caring for your body from the inside out. A balanced approach involving a thoughtful diet and avoiding smoke helps. This way leads to improved skincare and greater overall health for those with psoriasis.
Comprehensive Psoriasis Treatment Methods
Psoriasis treatment requires a personal plan. There are many options for patients, making it easier to find the right fit. The approach is based on the severity of itchy patches and how it affects life. A thorough evaluation leads to a better path towards healing.
Topical Psoriasis Medications and Moisturizers
Topical treatments are key for managing psoriasis. Medicines like creams and ointments, especially steroids and vitamin D, offer direct help. Moisturizers are also crucial as they hydrate the skin. This reduces dryness and prevents scales, common psoriasis symptoms.
Systemic Treatments and Biologic Therapies
For severe psoriasis, systemic treatments are needed. Drugs such as methotrexate and retinoids treat the whole body. Recent science has also brought biologic therapies. These target specific parts of the immune system that cause psoriasis.
There’s also light therapy, which slows the growth of skin cells. Every patient’s experience with psoriasis is different. The variety of treatments shows the dedication to personalized care for everyone’s needs.
FAQ
What exactly is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a skin condition that speeds up the life cycle of skin cells. This results in thick, scaly patches on the skin. These patches may itch or cause discomfort.
How does the immune system influence Psoriasis?
In Psoriasis, the immune system attacks healthy skin cells by mistake. This makes skin cells multiply quickly, creating scaly plaques.
Can I contract Psoriasis from someone else?
No, you can’t get Psoriasis from touching someone who has it. It’s not contagious.
What are the typical symptoms of Psoriasis?
Symptoms include red, inflamed skin with silvery scales, known as plaques. These can be itchy and painful. Psoriasis often affects the scalp, knees, elbows, and lower back.
How does Plaque Psoriasis differ from other types?
Plaque Psoriasis is the most common type. It presents as raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches can itch, hurt, crack, and bleed.
Are there other types of Psoriasis I should know about?
Yes, there are other types like Guttate, Inverse, Pustular, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis. Each type has unique features and affects the skin differently.
What causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis’s exact cause is unclear. It’s thought to stem from genetic factors and external triggers. These triggers lead to immune system overreactions, causing inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover.
How is Psoriasis diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose Psoriasis by looking at the skin and asking about family history. Sometimes, a biopsy or lab tests are needed to confirm it.
Is genetics a factor in Psoriasis?
Yes, genetics are important. People with certain genes are more likely to get Psoriasis. However, external triggers are also needed for it to develop.
What are common triggers that might cause a Psoriasis outbreak?
Triggers include skin injuries, stress, some medicines, and infections. Changes in weather can also cause outbreaks. Knowing and avoiding these triggers can help control Psoriasis.
How do lifestyle choices affect Psoriasis?
Smoking and drinking alcohol can worsen Psoriasis. Diet impacts it too. While no food cures it, anti-inflammatory foods may ease symptoms.
What treatments are available for Psoriasis?
Treatments range from creams and light therapy to systemic medicines. Severe cases might need biologic therapies. Lifestyle changes and natural remedies can also help.
How can I manage Psoriasis symptoms day-to-day?
Daily management includes using moisturizers, avoiding triggers, and following doctor’s advice. A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle also play a significant role.
Are there any alternative remedies for treating Psoriasis?
Some find aloe vera, oat baths, or capsaicin creams helpful. Still, these should complement, not replace, regular treatments. Always talk to your doctor first.
Does diet have an impact on Psoriasis?
No specific diet cures Psoriasis, but anti-inflammatory foods might reduce symptoms. Keeping a healthy weight can also lessen Psoriasis severity.