Aggression is a common behavior problem in dogs, and it is important to understand aggressive dog breeds for safety purposes. Certain dog breeds are known to exhibit aggressive traits, and being aware of them can help prevent potential incidents.
Dangerous dog breeds should be approached with caution and responsible ownership. By understanding the characteristics and behavior patterns of these breeds, you can ensure the safety of both humans and animals.
Key Takeaways:
- Aggression is a common behavior problem in dogs.
- Understanding aggressive dog breeds is crucial for safety.
- Be cautious when dealing with dangerous dog breeds.
- Responsible ownership is essential in managing aggression.
- By being aware of aggressive traits, you can prevent potential incidents.
The First Step in Dealing with Aggressive Behavior
The first step in effectively addressing aggressive behavior in dogs is to prevent further episodes. The safety and well-being of both humans and animals involved should be the top priority. This can be achieved by implementing a comprehensive behavior treatment plan that focuses on modifying both the behavior of the dog and its environment.
Modifying the dog’s behavior involves identifying and understanding the triggers that lead to aggressive outbursts. By creating a list of trigger situations, owners can take immediate steps to avoid these situations temporarily. This can help in managing aggression and preventing any potential harm.
Modifying the dog’s environment is equally important in preventing aggressive behavior. Immediate changes can be made to the environment to ensure that situations that trigger aggression are minimized or eliminated. For example, if a dog becomes aggressive when encountering other dogs during walks, the owner can change routes or adjust the walking schedule to avoid such encounters.
It is crucial to note that testing a dog’s tolerance by deliberately exposing it to trigger situations should be avoided. Even one aggressive incident can set back the progress made in modifying behavior. Therefore, it is essential to prioritize safety and focus on positive reinforcement techniques to encourage desirable behavior.
By implementing a thorough behavior treatment plan, owners can effectively prevent aggressive behavior in dogs and provide a safe and harmonious environment for both the dog and those around it.
| Preventing Aggressive Behavior – Key Steps |
|---|
| 1. Identify trigger situations and create a list. |
| 2. Make immediate changes to the environment to avoid triggers. |
| 3. Avoid testing the dog’s tolerance by deliberately exposing it to triggers. |
| 4. Focus on positive reinforcement techniques to encourage desirable behavior. |
Factors Contributing to the Escalation of Aggression
Aggression in dogs can escalate over time due to various factors. Understanding these contributing factors is crucial in effectively addressing and managing aggressive behavior. The reinforcement of aggressive behavior, inconsistent responses, fear and anxiety, and punishment-based training techniques are significant elements that can worsen aggression in dogs.
Reinforcement of Aggressive Behavior
Aggressive behavior can be reinforced when it leads to the desired outcome for the dog. For example, if a dog displays aggression towards a perceived threat, such as a person or another animal, and the target retreats, the dog may interpret this as a successful response and continue to display aggression in the future. This reinforcement strengthens the aggressive behavior and increases the likelihood of it occurring again in similar situations.
Inconsistent Responses
Inconsistent responses from the targeted recipient can contribute to the escalation of aggression in dogs. When a dog receives mixed signals or unpredictable reactions from humans or other animals, it can lead to frustration and confusion. This frustration can intensify the dog’s aggressive response as it tries to communicate its needs or protect itself. Consistency in handling and responding to the dog’s behavior is crucial to prevent the escalation of aggression.
Fear and Anxiety
Fear and anxiety can significantly impact the intensity of aggressive behavior in dogs. Both humans and dogs can experience fear and anxiety, and in the presence of these emotions, aggression may be triggered as a means of self-defense or attempting to gain control of a situation. Dogs that have a history of experiencing fear or anxiety are more prone to displaying aggressive behavior when they perceive a threat or feel overwhelmed. Addressing fear and anxiety through behavior modification techniques can help reduce aggression in these cases.
Punishment-Based Training Techniques
The use of punishment-based training techniques has been associated with an increase in aggressive behavior in dogs. Training methods that rely on punishment, such as physical corrections or the use of aversive tools, can create fear and anxiety in the dog. This fear and anxiety can lead to defensive aggression, as the dog may feel threatened by the training methods or associate certain actions or stimuli with punishment. Positive reinforcement-based training methods are generally more effective in promoting desired behaviors and reducing aggression.
To effectively address and manage a dog’s aggressive behavior, it is essential to understand and consider these contributing factors. By focusing on positive reinforcement, consistent responses, and addressing fear and anxiety, it is possible to reduce aggression and promote a safer and more harmonious relationship between humans and dogs.
Duration and Safety in Behavior Modification
The duration of preventing exposure to trigger situations plays a crucial role in managing aggression in dogs. The length of time required for exposure prevention may vary depending on factors such as the dog’s personality, comfort level, and the type of aggression displayed. It is essential to work with a behavior consultant to assess the overall prognosis and risk associated with the dog’s aggression.
To address and modify aggressive behavior, behavior modification techniques such as desensitization and counterconditioning can be incorporated into the treatment plan. Desensitization involves gradually exposing the dog to the trigger situation in a controlled manner, starting with a minimal level of exposure and progressively increasing it over time. This gradual approach helps the dog become more comfortable and less reactive to the trigger.
Counterconditioning, on the other hand, aims to change the dog’s emotional response to the trigger situation. By pairing the trigger with something positive, like treats or praise, the dog starts to associate the trigger with a positive experience, ultimately reducing their aggressive response. Both desensitization and counterconditioning require consistency, patience, and professional guidance to ensure effectiveness.
However, it is important to note that some trigger situations may need to be permanently avoided or managed to ensure the safety of all parties involved. Working closely with a behavior consultant will help determine which situations can be safely reintroduced and which should be permanently avoided.
The Benefits of Duration and Safety in Behavior Modification:
• Increased comfort and reduced reactivity
• Promotes a positive emotional response to trigger situations
• Gradual improvement in the dog’s behavior and overall well-being
• Enhanced safety for both the dog and those around them
By prioritizing duration and safety in behavior modification, dog owners can significantly improve the quality of life for their pets while ensuring a safe environment for everyone.
| Duration and Safety in Behavior Modification | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Prevention of exposure to trigger situations | Increased comfort and reduced reactivity |
| Desensitization and counterconditioning | Promotes a positive emotional response to trigger situations |
| Permanent avoidance or management of trigger situations | Gradual improvement in the dog’s behavior and overall well-being |
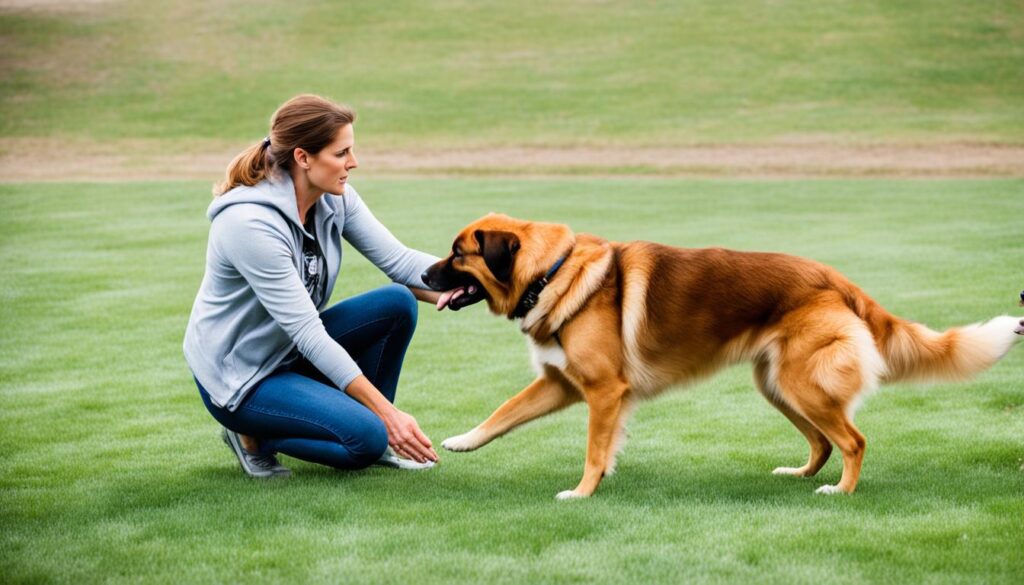

Safety Measures for Aggressive Dogs
When dealing with aggressive dogs, it is essential to prioritize safety for both humans and the dogs themselves. Various management tools can be used to improve safety and minimize the risk of aggressive incidents. These tools, when used properly and under supervision, can help in handling and training aggressive dogs.
Leash or Tether
One effective management tool is a leash or tether, which can be used to control and restrain the dog at a safe distance from potential triggers. This allows for better control and prevents the dog from engaging in aggressive behaviors. It is important to choose a sturdy leash or tether that can handle the dog’s strength and size.
Crates and Confinement
Crates and confinement can provide a secure area for the dog, creating a safe space where they can be confined when necessary. This helps prevent aggressive interactions in certain situations, such as when visitors are present or during high-stress situations. It is crucial to ensure that the crate is the appropriate size for the dog and that it is comfortable and safe.
Basket Muzzle
A basket muzzle can be a valuable tool in preventing the possibility of a bite. It allows the dog to breathe and pant comfortably while still preventing them from biting. Basket muzzles are designed to allow the dog to eat, drink, and pant without any restriction. It is important to acclimate the dog to the muzzle gradually and ensure it fits properly for maximum safety.
Head Halter
A head halter can be used to redirect the dog’s focus away from triggers and promote better control during walks or interactions. The head halter fits over the dog’s muzzle and head, providing control similar to that of a horse’s halter. It allows the handler to guide the dog’s movements and prevent them from lunging or reacting aggressively to stimuli. Proper fitting and gradual introduction to the head halter are crucial for the dog’s comfort and safety.
When using these management tools, it is important to prioritize safety and to follow proper training guidelines. Consulting with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide guidance on the appropriate use of these tools and help address any specific concerns or challenges.
| Management Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Leash or Tether | Control and restrain the dog at a safe distance from potential triggers |
| Crates and Confinement | Create a secure area to prevent aggressive interactions in certain situations |
| Basket Muzzle | Prevent the possibility of a bite while allowing the dog to breathe and pant comfortably |
| Head Halter | Redirect the dog’s focus and promote better control during walks or interactions |
Conclusion
Understanding and managing aggression in dog breeds is crucial for the safety of both humans and animals. Aggressive dog breeds can present unique challenges, but with the right safety tips and responsible ownership practices, it is possible to create a safe and harmonious environment.
Preventing exposure to trigger situations is key in handling and training aggressive dogs. By identifying and avoiding situations that can provoke aggressive behavior, owners can minimize the risk of incidents and ensure the safety of everyone involved.
Additionally, using management tools such as leashes or tethers, crates and confinement, basket muzzles, and head halters can enhance safety when dealing with aggressive dogs. These tools, when used responsibly and under supervision, provide an extra layer of protection and help redirect the dog’s focus away from potential triggers.
Responsible ownership is pivotal in addressing aggression in dog breeds. Spaying/neutering and socializing dogs from an early age are essential steps in preventing and managing aggressive behavior. By taking these measures and following the provided safety tips, we can promote responsible ownership and create a secure and peaceful environment for everyone.
FAQ
What are some aggressive dog breeds to avoid?
Some aggressive dog breeds to avoid include Pit Bulls, Rottweilers, German Shepherds, Doberman Pinschers, and Chow Chows. These breeds are known for their aggressive traits and require experienced owners.
How can I prevent further episodes of aggressive behavior in my dog?
The first step in preventing further episodes of aggressive behavior is to ensure the safety of everyone involved. Modifying the behavior and the environment is crucial. Immediate changes can be made to avoid situations that trigger aggression. Creating a list of trigger situations and avoiding them temporarily can help manage aggression.
What factors contribute to the escalation of aggression in dogs?
Aggressive behavior can escalate due to various factors. Reinforcement of aggressive behavior, inconsistent responses from the targeted recipient, fear and anxiety in both humans and dogs, and the use of punishment-based training techniques can all intensify aggression in dogs.
How long should I prevent exposure to trigger situations in behavior modification?
The duration of preventing exposure to trigger situations may vary depending on the dog’s personality, comfort level, and type of aggression. Behavior modification techniques such as desensitization and counterconditioning can be included in the treatment plan. Some trigger situations may need to be permanently avoided or managed to ensure safety.
What are some safety measures for dealing with aggressive dogs?
Various management tools can be used to improve safety when dealing with aggressive dogs. These include a leash or tether to restrain the dog at a safe distance, crates and confinement to provide a secure area, a basket muzzle to prevent biting, and a head halter to redirect the dog’s focus away from triggers. It is important to use these tools safely and under supervision.